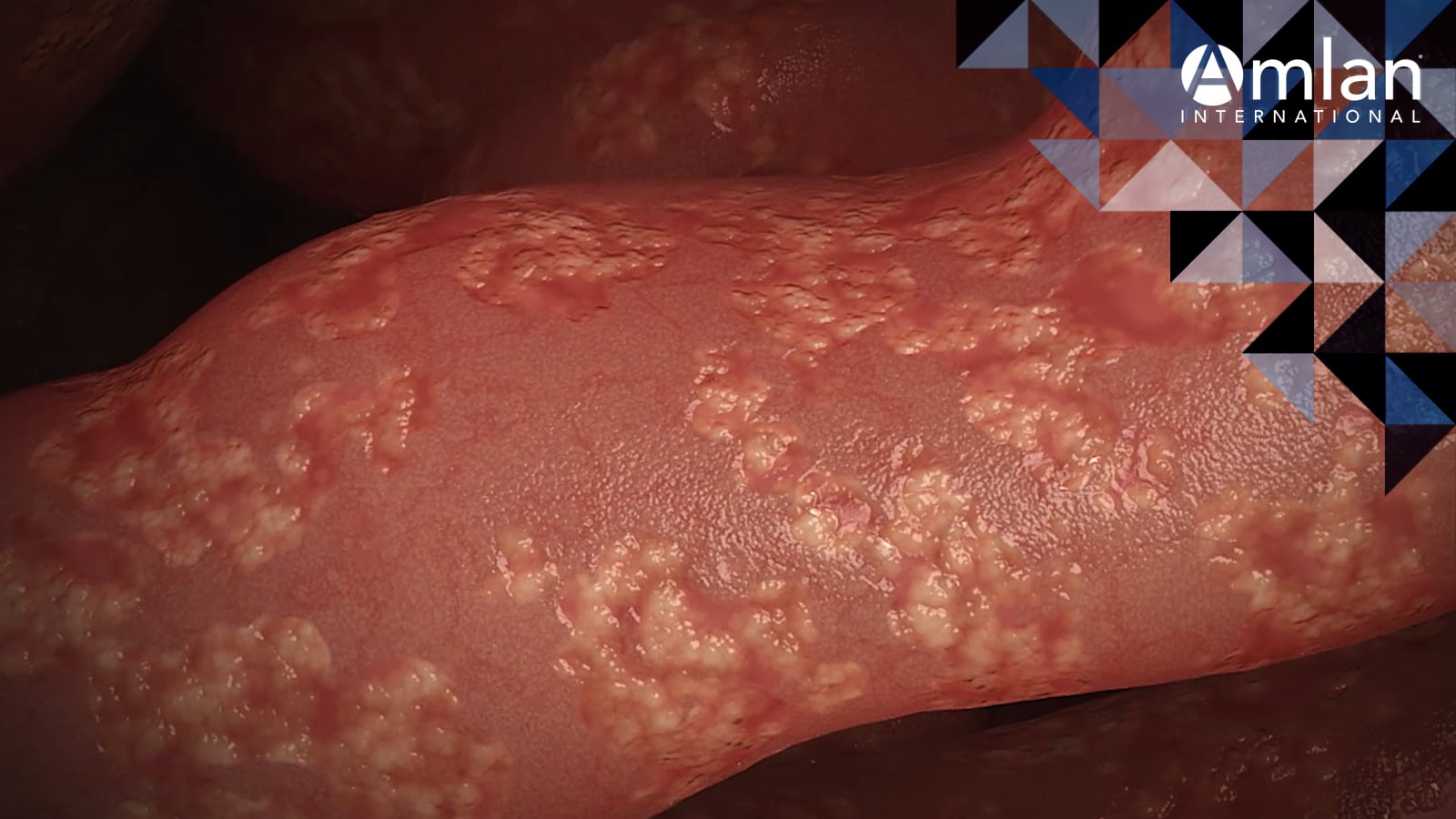
Necrotic enteritis is a common infectious disease that costs the poultry industry billions of dollars each year. With more and more poultry production systems moving toward the global objective of reduced in-feed use of antibiotics for growth promotion, maintaining a healthy intestinal environment now relies more heavily on other management methods to reduce the risk of necrotic enteritis development. Keep reading to learn more about the origins of necrotic enteritis, the relationship between necrotic enteritis and coccidiosis, and management of the disease risk in ABF production systems.
C. perfringens: The Cause of Necrotic Enteritis
Necrotic enteritis is caused by Clostridium perfringens types A and C: gram-positive, spore-forming anerobic bacteria. C. perfringens can be found throughout the poultry house environment and has spores which, under the right environmental conditions, can survive for long periods outside the bird. The normal microbiota of the bird contains C. perfringens, so its presence alone doesn’t necessarily indicate an issue. Instead, disease occurs when predisposing conditions in the bird cause overgrowth of the pathogen. There are multiple factors that can contribute to C. perfringens overgrowth including diet changes, immune status and stress, intestinal pathophysiology and concurrent infection with coccidiosis.
Multiple exotoxins can be produced by C. perfringens, including alpha-toxin and necrotic enteritis toxin B-like toxin (NetB). Alpha-toxin is cytotoxic to endothelial cells, red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets, whereas NetB toxin forms pores in cell membranes that allows electrolytes to rupture cells, causing cell death and necrotic lesions in the small intestinal mucosa. These two toxins are known to have a role in necrotic enteritis development.
Impaired Nutrient Adsorption
In healthy birds, the epithelium and mucus layer of the intestine form a selective barrier between internal tissues and the external environment (the intestinal lumen). The natural barrier allows nutrients through the intestinal wall but not pathogens and their biotoxins. When there is an overgrowth of C. perfringens, there is a breakdown of the defensive barrier. The damage to the intestinal wall hinders nutrient digestion and absorption and can allow toxins to enter the circulatory system.
Necrotic enteritis can present as either clinical or subclinical disease. The clinical form is characterized by high mortality, whereas subclinical disease causes decreased weight gain and increased feed conversion ratio (FCR). The increased FCR is due to the reduced nutrient digestibility and adsorption, resulting in compensatory feed intake.
Coccidiosis Can Increase Necrotic Enteritis Incidence
Coccidiosis is another common disease in poultry that causes a significant negative economic impact on production. It is an enteric disease caused by parasitic protozoa in the Eimeria genus. Part of the Eimeria life cycle includes invading intestinal epithelial cells, damaging the intestinal wall barrier. The damage that coccidia cause to intestinal epithelial cells promotes invasion by C. perfringens (as well as other pathogens), increasing the incidence of necrotic enteritis.
Necrotic Enteritis in Antibiotic-Free Production
Managing necrotic enteritis in an ABF production system requires detailed strategies including the use of vaccinations, diagnostic tools and natural feed additives. In some production systems, ionophores used to control coccidiosis may also be eliminated, which further heightens the importance of other management practices that keep birds free of diseases like coccidiosis and necrotic enteritis.
Management practices, such as biosecurity, sanitation, water quality and air quality, also require increased planning and monitoring in ABF systems. Reduced ventilation, increased litter moisture and poor husbandry can increase the incidence of necrotic enteritis. The quality and sanitation of eggs in the hatchery also needs to be managed well in ABF systems, so that birds have a healthy start to life.
Necrotic Enteritis Control Solutions
Along with management best practices, natural feed additives such as Varium® and Calibrin®-Z are available to help reduce the incidence of necrotic enteritis. Varium, a natural patented mineral-based feed formulation, can reduce challenges from pathogenic bacteria and their toxins, strengthen the intestinal barrier and activate the innate immune system to naturally defend against disease. In high challenge environments, Calibrin-Z, a broad spectrum biotoxin control feed additive, can be used on top of Varium to reduce the level of pathogens in the intestines that cause mortality, wet droppings, reduced feed efficiency and damage the integrity of the intestine.
Necrotic enteritis is a challenging disease for poultry producers, particularly those using an ABF production system. However, with best practice management strategies and inclusion of feed additives that promote intestinal health and function, poultry flock health can be improved, thereby reducing the risk of disease and maximizing production efficiency. To learn more about necrotic enteritis, keep checking the Education Center for other posts in the necrotic enteritis series.
Reference
Chi, F. A Viable Adjunct or Alternative to Antibiotics: Meta-Analysis of Broiler Research Shows Natural Growth Promoter Delivers Feed Efficiency Equal to Antibiotics, Amlan International. https://amlan.com/product-category/feed-efficiency/