Product availability may vary by country, associated claims do not constitute medical claims and may differ based on government requirements.
In some countries, the use of zinc bacitracin as an antibiotic growth promoter (AGP) in poultry is restricted due to concern over the increase in multi-drug-resistant bacteria that do not respond to traditional antibiotic treatments. Restrictions in the use of AGPs in animal feeds like zinc bacitracin has spurred the development of natural AGP alternatives that keep birds healthy and growing efficiently.
Natural Performance Promotion
Varium® is a patented natural mineral-based feed additive that promotes efficiency and productivity in poultry. Unlike antibiotics that kill bacteria, the patented technology in Varium includes a synergistic formulation of ingredients that binds pathogenic bacteria and their toxins, provides an energy source for the growth of healthy and strong enterocytes and gently stimulates immunity cells. With multiple modes of action, Varium adds value for producers by replacing the need for multiple feed additives; it can provide the same benefits in one product thereby simplifying diet formulations and reducing costs.
Comparing Varium with Zinc Bacitracin
To demonstrate its effectiveness, Varium was directly compared to zinc bacitracin in a broiler study conducted by a university in Pakistan. In the trial, 180 Ross 308 chicks (10 chicks per pen, 6 pens per treatment) were randomly allocated to one of three treatment groups: control (0.01% zinc bacitracin), Varium 0.1 (0.1%) or Varium 0.15 (0.15%). The broilers were raised under normal production conditions, with the trial ending on day 35. Newcastle disease vaccine was administered to all birds on day 6 (intraocular and subcutaneous) and a booster (oral) was administered on day 21. Newcastle disease titers were measured on days 20 and 35 from 18 birds per treatment. Three birds per pen (18 total per treatment), randomly selected on day 35, and had small intestine morphology and bacterial counts in the small intestine and digesta measured.
Varium Protects Intestinal Health
The study showed that Varium was able to protect intestinal morphology better than zinc bacitracin. In Varium-fed broilers, a significant dose-response effect was observed for intestinal (jejunum) villus height and villi index (villus height to crypt depth) on day 35, with all Varium treatments significantly higher than the zinc bacitracin control (Figure 1). A similar dose response was observed with intestinal (jejunum) crypt depth; all Varium treatments were significantly lower than the control, and Varium 0.15 was significantly lower than Varium 0.1 (Figure 1).
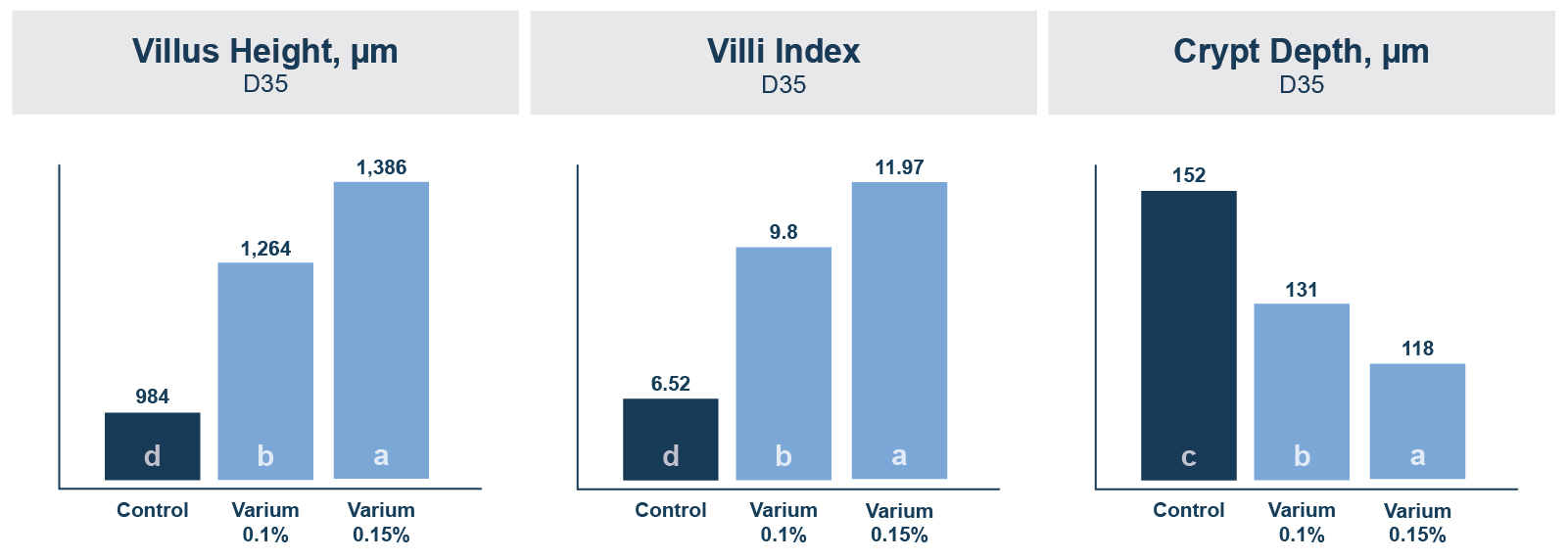
Varium was also able to protect the birds from necrotic enteritis to the same extent as zinc bacitracin. Necrotic enteritis was not found among any of the sampled birds on day 35. Lesion scores (0 to 4 scale) for the entire length of the small intestine were not different between treatments; however, Varium 0.1 had a better effect on intestinal elasticity than the other treatments.
Beneficial Bacteria Increase with Varium
Varium was able to promote colonization of beneficial bacteria while decreasing the population of pathogenic bacteria. Varium 0.1 had significantly more beneficial Lactobacilli than zinc bacitracin and Varium 0.15 had significantly more than all treatments (Figure 2). All Varium treatments decreased the population of Salmonella in the small intestine and digesta compared to zinc bacitracin (Figure 3).
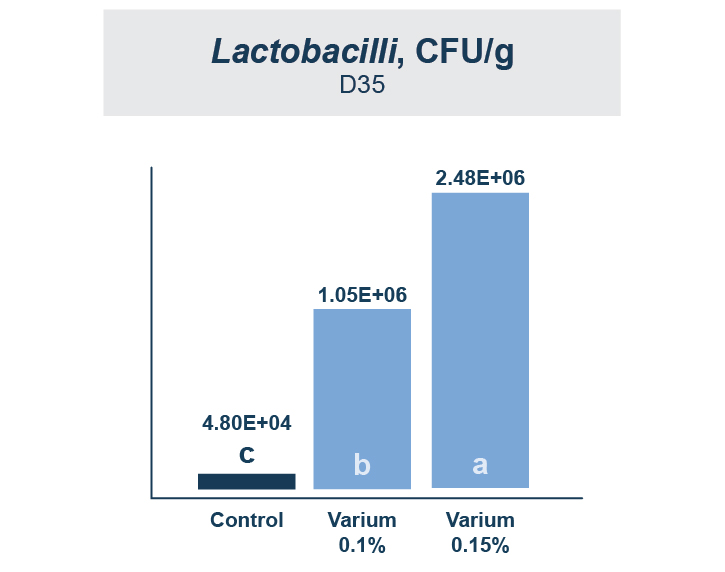
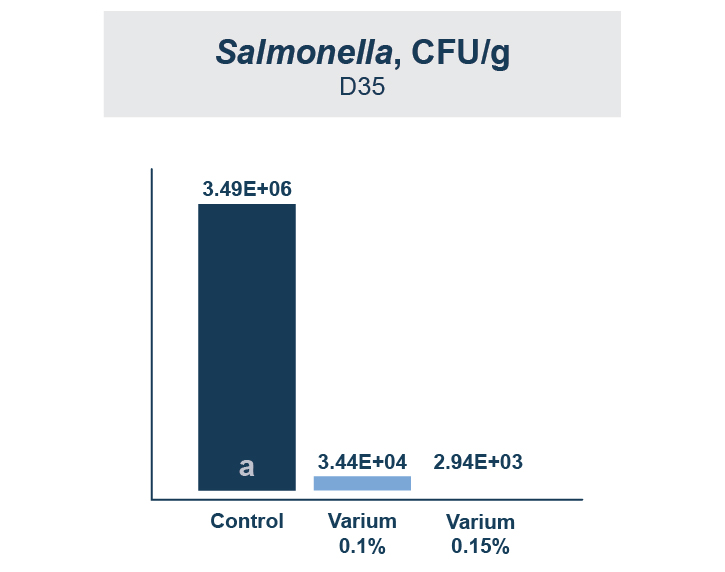
A Better Immune Response
Varium also improved the immune response to vaccination. On day 20 and 35, Newcastle disease antibody titer (hemagglutination inhibition test) was significantly higher in all Varium treatments compared to zinc bacitracin. Previous research (contact Amlan for more details, info@amlan.com) has shown that feeding Varium during disease challenge can restore the expression of immune cells that are responsible for stimulation of an antigen-specific immune response and also increase phagocytic activity compared to the control group. This increased immune response, as well as the removal of bacterial toxins that can cause immunosuppression, are thought to be the reasons behind the increase in Newcastle disease antibody titers observed in the present study.
This study confirmed that Varium can be as effective as zinc bacitracin in promoting intestinal health. The doses of Varium at 0.1 and 0.15% performed equal to or better than zinc bacitracin for the parameters tested. For more information on how Varium can improve health, production efficiency and value, visit the Varium product page.

