With cutting-edge equipment and state-of-the-art facilities, Amlan’s talented Life Sciences team creates value-adding mineral-based products for poultry and livestock producers. The Richard M. Jaffee Center for Applied Microbiology houses the specialized equipment used by the Life Sciences team who draw upon their extensive research experience and knowledge base to create novel, natural solutions that improve poultry and livestock health and production efficiency.
Life Science Experts
The Amlan research team is led by Life Sciences Director Hongyu Xue MD, PhD, an experienced scientist in clinical and animal nutrition, who brings a unique point of view to Amlan’s research by leveraging his expertise in human medicine. Dr. Xue has a background in academic medicine and research that cross-links gastroenterology, immunology, microbiology and nutrition. Working with Dr. Xue is a multi-disciplinary team of scientists with expertise across microbiology, animal nutrition, chemistry and material science areas. Several members of the Life Sciences team were recently featured on an episode of “Built in America: INNOVATION NATION” on the Fox Business Network, where they showcased some of their novel research.
Cutting-Edge Equipment
The state-of-the-art equipment in the Richard M. Jaffee Center for Applied Microbiology allows the Life Sciences experts to use a variety of research techniques to develop and assess new mineral-based products for the animal health market.
The Life Sciences team enhances Amlan’s unique mineral to develop natural solutions that can control the microbial pathogens that negatively impact the health and productivity of poultry and livestock. To do this, the scientists study these pathogens and their toxins to understand their physiology and mode of action. Some pathogens require anerobic conditions to survive, so these pathogens are cultivated in Amlan’s anerobic chamber — a more efficient and robust method than alternative techniques such as anerobic jar or pouch systems.
Conditions within the chamber can perfectly mimic the anerobic environment of the distal gastrointestinal (GI) tract (e.g., ileum and cecum) which serves as the primary colonization site for a vast variety of common microbial pathogens for poultry and livestock. The anaerobic chamber is of tremendous value to help Amlan’s scientists cultivate and further characterize the target pathogens and select commensal microbial populations colonizing the distal GI tract. Further, the chamber also enables the scientists to screen novel products in development and evaluate their antimicrobial effects for certain anaerobic pathogens. Novel strains of beneficial bacteria (probiotics) can also be isolated, grown and tested in the anerobic chamber. The photo below shows an example of the zone of inhibition surrounding an Amlan-developed probiotic (right) versus a water control (left).

Further assessment of the new products can be conducted using equipment such as an ICP-OES (inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometer) that allows the team to examine how different cations released by Amlan’s unique mineral affects bacterial virulence. Some metals (cations) are known to suppress the expression of virulence genes in bacterial pathogens.
The lab also includes a fluorescent microscope that enables microbes to be observed instantly to see a product’s effect on bacterial morphology and viability.
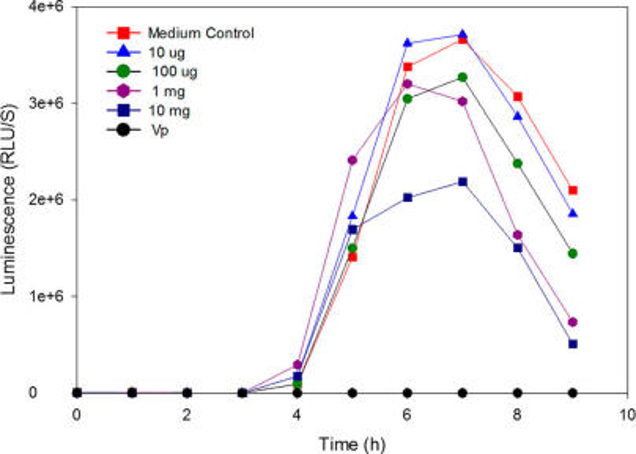
Using real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR), the Life Sciences team have developed methods to detect toxin genes from microbial pathogens that can have negative effects on poultry and livestock production. Using this information, natural solutions can be developed that disarm these pathogens and help protect birds and animals from disease. For example, real-time PCR is used to investigate the effects of new products on pathogen virulence gene expression. Further, this technology can help determine the copy numbers of specific virulence genes and help make an early diagnosis of specific enteric diseases in poultry and livestock.
The Richard M. Jaffee Center for Applied Microbiology is named after the former chairman of Oil-Dri Corporation of America, doing business as Amlan International. Jaffee’s pioneering spirit and vision for Oil-Dri to conduct research in the life sciences is the influence behind Amlan’s focus on developing value-added next-generation animal health products.
To learn more about the research behind Amlan’s natural and efficacious products, visit https://amlan.com/blog/category/research-studies/.